Introduction:
In the realm of energy-efficient and high-performance windows, triple glazing has emerged as a cutting-edge solution that goes beyond the traditional double-glazed counterparts. The concept of adding a third layer of glass to windows has transformed the way we approach insulation, sound reduction, and overall energy efficiency in our homes and buildings. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies and advantages of triple glazing windows, shedding light on why they are becoming increasingly popular in the realm of modern construction and renovation.
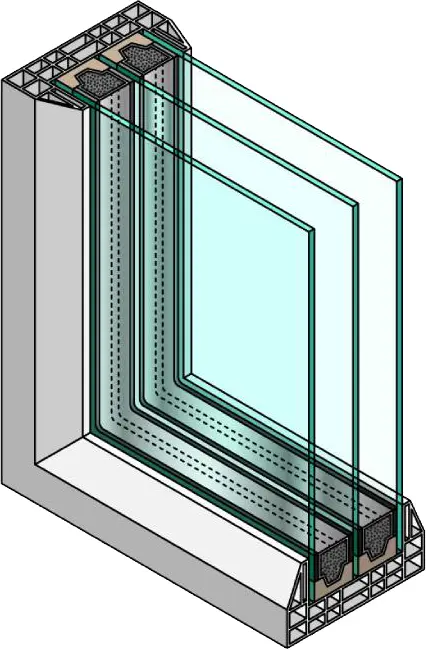
Understanding Triple Glazing:
Triple glazing, as the name suggests, involves the use of three layers of glass within a single window unit, separated by insulating spaces filled with air or gas. This design aims to enhance the thermal and acoustic performance of windows, offering a range of benefits that surpass those provided by double glazing.
- Enhanced Thermal Insulation: The primary advantage of triple glazing lies in its superior thermal insulation properties. The additional layer of glass creates two insulating air or gas pockets, minimizing heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a building. This results in improved energy efficiency, reduced heat loss during colder seasons, and better temperature regulation throughout the year. Homeowners benefit from lower energy bills and a more comfortable living environment.
- Sound Reduction: Triple glazing excels not only in thermal insulation but also in sound reduction. The multiple layers of glass, along with the insulating gaps, create a barrier that helps dampen external noise. This is particularly beneficial for homes located in noisy urban areas or near busy streets, providing occupants with a quieter and more peaceful living space.
- Condensation Control: The additional layers of glass in triple glazing contribute to minimizing condensation on the interior surface of windows. Condensation occurs when warm air meets a cold surface, leading to moisture buildup. With the enhanced insulation of triple glazing, the interior glass surface remains closer to room temperature, reducing the likelihood of condensation. This is especially advantageous for maintaining a clear view and preventing potential damage to window sills and frames.
- Increased Energy Efficiency: Beyond thermal insulation, triple glazing significantly improves the overall energy efficiency of a building. The reduced reliance on heating and cooling systems translates into lower energy consumption, contributing to both environmental sustainability and cost savings for homeowners. Many triple glazing units also feature Low-E (low emissivity) coatings, further optimizing their energy performance.
- Environmental Sustainability: The focus on sustainability in construction has led to an increased interest in environmentally friendly building materials and practices. Triple glazing aligns with this trend by promoting energy efficiency, reducing carbon footprints, and supporting the creation of energy-efficient buildings. As awareness of climate change grows, triple glazing becomes a key player in the push towards greener and more sustainable living spaces.
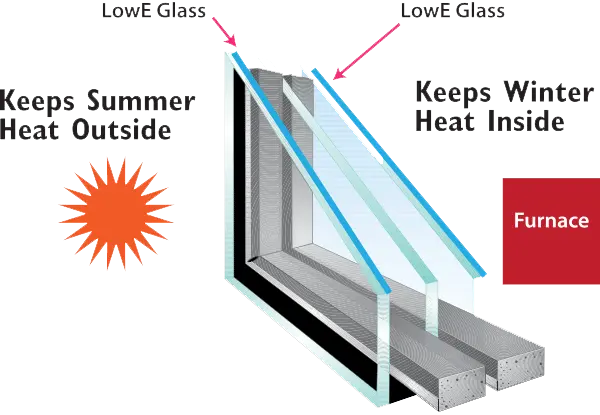
Conclusion:
As we conclude our exploration into the world of triple glazing windows, it is evident that these advanced window solutions offer a comprehensive array of benefits. “Beyond Double: The Ins and Outs of Triple Glazing Windows” has guided us through the intricacies of enhanced thermal insulation, sound reduction, condensation control, increased energy efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
Triple glazing is not just a technological advancement; it represents a shift towards more conscious and efficient building practices. As we celebrate the 1-year anniversary of delving into the wonders of triple glazing, it is clear that these windows have firmly established themselves as a cornerstone in the evolution of energy-efficient and high-performance building solutions. Whether in new constructions or retrofitting existing structures, triple glazing windows are paving the way for a brighter, quieter, and more sustainable future in modern architecture.

